Food allergies, drug allergies, and skin allergies are very common occurrences, but have you heard about toothpaste allergy? This condition is quite rare but it can still happen. Here are some of the important things to know about toothpaste allergy.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Toothpaste Allergy?
Signs of an allergic reaction may vary depending on the ingredients you are sensitive to and the severity of your reaction.
While there are reports of allergies linked to toothpaste, these reports are seldom. The ingredients used in toothpaste have changed over time and companies continue to improve their formulas to make their products more effective and safer.
One commonly reported an allergic reaction to toothpaste is cheilitis, a severe form of chapped lips. It may be accompanied by a rash surrounding the mouth. With that said, flavorings that are used in toothpaste such as peppermint oil may be the culprit of this adverse reaction. For instance, a 1998 report described a case of a patient who had cheilitis due to contact allergy to spearmint oil that was found in the toothpaste. Such reactions will resolve when you change to a different brand or flavor of toothpaste.
Toothpaste may contain several potential allergens. These include fluoride, flavorings, fragrances, dairy, and gluten. Cinnamon derivatives were a common allergy cause to toothpaste. A study has shown that cinnamic aldehyde, a widely used flavoring agent in mouthwash, lip sunscreen and toothpaste, played a role in causing intraoral allergic contact dermatitis.
How to Diagnose a Toothpaste Allergy
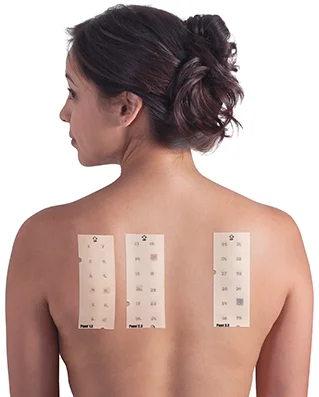
T.R.U.E Patch Test
To diagnose a toothpaste allergy, a patch test is performed. This is done with a paper tape system, like the T.R.U.E Test. Thin-Layer Rapid Use Epicutaneous (TRUE) Patch Test is a convenient testing for the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis. This is the only FDA-approved test for contact dermatitis in the US. This patch testing is an easy, simple procedure to identify the causative agent of the allergy. Every test units consist of 3 panels containing various chemicals.
The results are interpreted after 48 hours and again at 72 and 96 hours after placement. A positive result is confirmed if there are redness, blisters and mild swelling at the specific site of the chemical in question. This site often itches and appears red, although the size of the site is very small.
What to Do If You Suspect a Toothpaste Allergy
If you noticed severely chapped lips, irritated lips or rashes around your mouth and you think your newly bought toothpaste is the culprit, stop using that toothpaste, switch to a new brand and check if the symptoms subside.
If you are indeed allergic to an ingredient in the toothpaste, there are many toothpastes that are fluoride-free and unflavoured. A toothpaste allergy should not hinder you for having convenient, safe and great oral hygiene.
Once you found out what you are allergic to, it will be easier for you what to avoid when choosing the oral care products.